Water Discharge Guidelines and Standards at Telkom University
Telkom University is committed to maintaining environmentally friendly waste and water discharge management practices that comply with national guidelines. The campus incorporates various treatment sy...
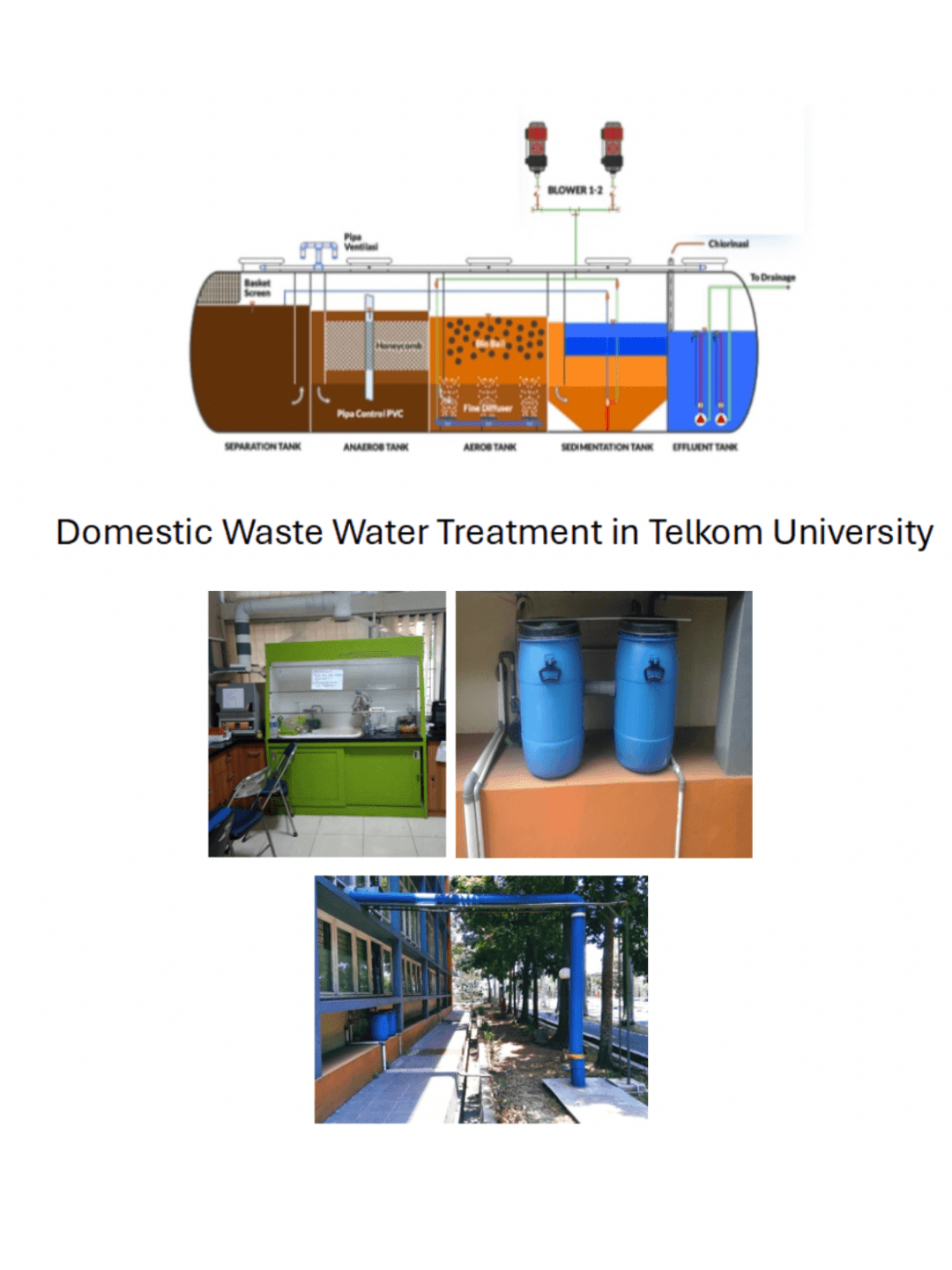
Telkom University is committed to maintaining environmentally friendly waste and water discharge management practices that comply with national guidelines. The campus incorporates various treatment systems for domestic, chemical, and medical wastewater to ensure all discharge meets quality standards and minimizes environmental impact. Here’s an overview of Telkom University’s guidelines, systems, and standards in place to manage water discharge:
Domestic Wastewater Treatment
Telkom University has 34 septic tanks that treat domestic wastewater originating from toilets using both aerobic and anaerobic processes. The aerobic system utilizes living microorganisms that work in the presence of oxygen, while the anaerobic process occurs in oxygen-free conditions. The purpose of these treatments is to produce odorless, clear water. The final chamber of each septic tank produces treated water that is then repurposed for watering plants around the campus, supporting water reuse initiatives and reducing water waste.
Sewage Treatment Plant Process
Telkom University operates a sewage treatment plant designed to meet quality discharge standards. The primary goals are odor control and clarity, ensuring that treated water does not negatively impact the campus environment. This system highlights Telkom University’s commitment to sustainable water management practices and its dedication to reducing its environmental footprint.
Furnace Wastewater Neutralization Process
In addition to domestic wastewater, Telkom University also processes chemical waste generated from furnace operations, which produce both gas and liquid waste. Figure 1 illustrates the waste treatment process, which is divided into two types:
- Gas Waste:
- During furnace operation, combustion gases are drawn through an exhaust pipe into a grounding tank.
- Additionally, after cleaning chemical containers or measuring cups, a pump system is used to ensure the proper disposal of any residues.
2. Liquid Waste:
- Liquid chemical waste generated from the furnace process is collected in a reservoir (jerry can). The final treatment of this waste occurs through liquid waste processing system.
- After experiments, measuring cups or testing containers are cleaned in a sink that feeds into a reservoir containing a calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) solution to neutralize any remaining chemicals.
- Once the reservoir is full, the liquid waste is transferred to the grounding tank for further processing and disposal.
All hazardous chemical waste from laboratory experiments is managed in strict accordance with waste disposal procedures, ensuring compliance with laboratory waste management standards.
Medical Waste Treatment Partnership
In collaboration with PT. Tenang Jaya Sejahtera, Telkom University's Pratama Telkomedika Clinic follows established guidelines for medical waste disposal. This partnership complies with Indonesia's Ministry of Environment Regulation No. Kep-58/MENLH/12/1995, which sets effluent standards for hospital and clinic activities.
Telkom University’s comprehensive approach to water discharge management highlights its commitment to sustainability and environmental responsibility. Through the use of advanced wastewater treatment systems, partnerships, and adherence to regulatory standards, the university ensures that all waste discharge — whether domestic, chemical, or medical — is carefully managed and treated. These efforts contribute to a cleaner, safer campus environment and reflect Telkom University’s dedication to sustainable practices.